Why Your Laboratory Requires an Electronic Lab Notebook
Documentation is of utmost essence in the scientific field.
This is especially true for laboratories that conduct several experiments on a daily basis.
Be it collecting raw data from instruments, or writing values from tests, the process of physically noting down crucial information onto paper can quickly become challenging.
Not to mention messy as well.
Experiments of the same type cannot be easily sorted or tagged — even if you consider stapling them as an option, it quickly becomes infeasible when the number of experiments are more than 100 or so.
This is where digital recordkeeping comes in.
No matter who you are, a researcher, a lab analyst, or a chief scientist, or just someone who has just forayed into the academic/research field, the hassle due to paper-based note-keeping is a real headache.
An Electronic Lab Notebook is a form of specialized software that deals with exactly this: eliminating paper-based data collection and collation, while also enabling much more.
Keep reading to find out.
What is an Electronic Lab Notebook?
If you are a scientist, engineer, researcher or a laboratory professional, an Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) is a software system made for you, to assist with recording, organising and managing various documentation like test results, experimental data and notes on your procedures, tasks, etc. It typically provides you with features such as data tables, mathematical & chemical formulas and equations. It also allows you to connect with laboratory devices and instruments for real-time data collection and analysis.
Any device with internet connectivity is enough to help you access modern ELNs remotely and can aid in collaboration, data sharing, and compliance with regulations. In its simplest form, your messy and hard-to-maintain paper laboratory notebooks get an upgrade when you replace them with an Electronic Lab Notebook.
Core Functionalities of Electronic Lab Notebook – What Can it Offer?
A modern Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) offers you a range of core functionalities aimed at enhancing the efficiency, organization, collaboration, and reproducibility of your laboratory research. Some of the key capabilities include:
Digital Note-taking: Electronic Lab Notebooks assist researchers to record experimental procedures, observations, and results digitally, replacing traditional paper notebooks. This allows you to create text notes, draw diagrams, and attach multimedia files such as images, videos, and documents.
Structured Data Entry: Like other documentation software such as Microsoft Word or Excel, Electronic Lab Notebooks provide templates and forms for structured data entry, having pre-defined prompts for each section of your research. It aids in keeping your experimental parameters, sample information, and metadata consistent and organised while ensuring standardisation and facilitating proper data analysis.
Integration with Laboratory Instruments and Software: They offer integration with laboratory instruments and software tools, allowing data import/export, automated data capture, and seamless workflow integration. This encourages teamwork & data acquisition and enhances reproducibility.
Version Control: Electronic Lab Notebooks offer version control features that track changes made to your entries over time. Version control lets you see and review previous versions of your entries. This lets you compare alterations, analyse how your experiments and analysis evolved, and even revert if needed.
Search and Retrieval: Electronic Lab Notebooks comprise robust search functionalities to quickly locate specific experiments, protocols, or data sets within your notebook. Search by keyword, filter by details like date or sample type, or use advanced options for a laser-focused hunt. No more wasted time scouring pages, for your research is always at your fingertips in an ELN.
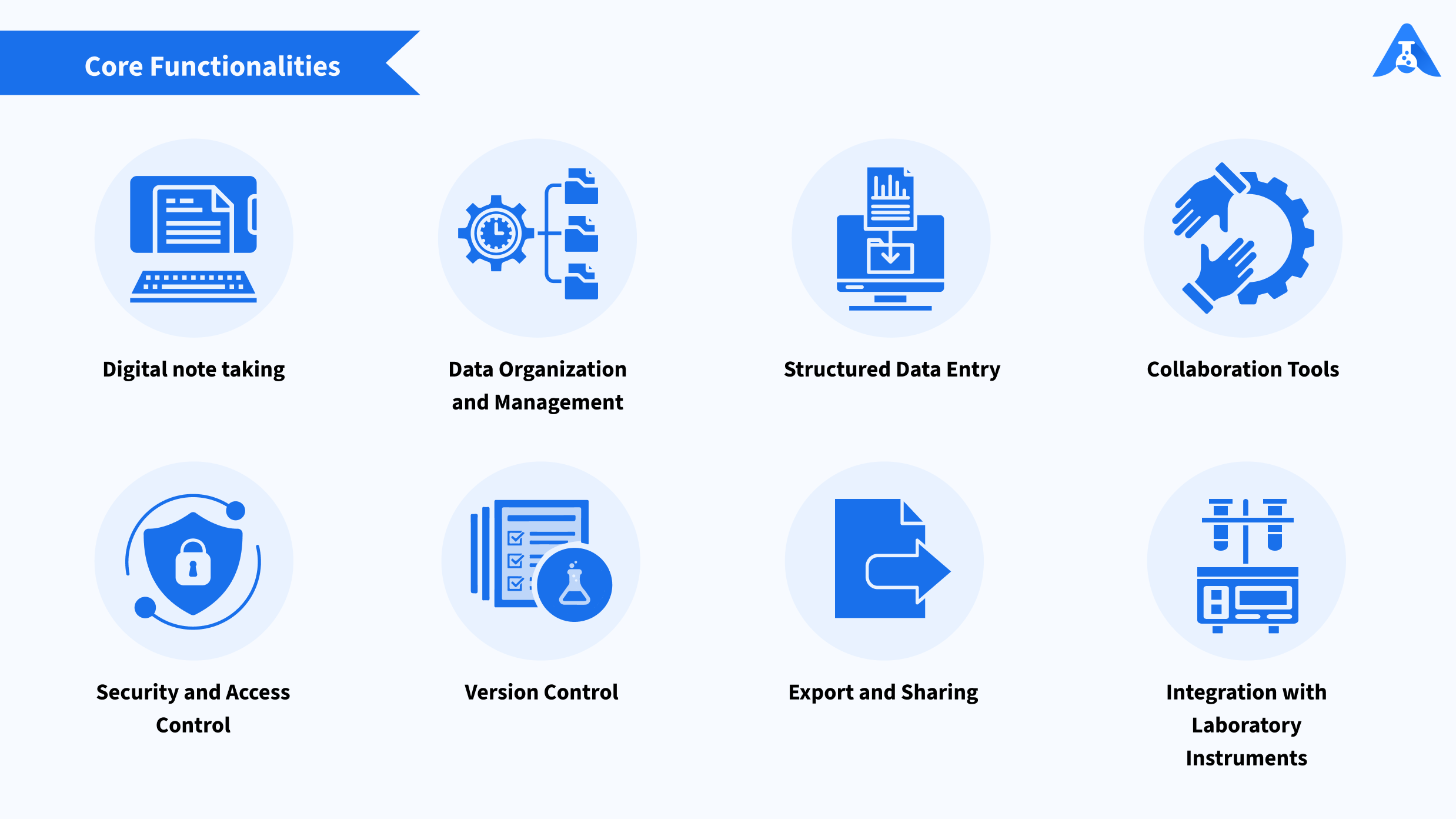
Data Organization and Management: Electronic Lab Notebooks enable the organization of your experiments into logical structures such as projects, experiments, or folders. Researchers can categorize and tag entries for efficient data management and retrieval.
Collaboration Tools: Electronic Lab Notebooks support collaboration among team members by allowing shared access to your notebooks, entries, and data sets. Your collaborators can view, comment on, or contribute to your experiments in real time.
Security and Access Control: Electronic Lab Notebooks prioritise your data security and compliance by implementing features such as user authentication, access control, encryption, and audit trails. Your sensitive research data remains protected in the vault-like environment of your ELN and ensures regulatory compliance.
Export and Sharing: Electronic Lab Notebooks enable you to export your data and entries in various formats. This makes it easy to share your findings with collaborators, supervisors, or regulatory agencies, ensuring everyone has the information they need in the format they prefer.
Overall, a modern Electronic Lab Notebook serves as a comprehensive digital platform for you to document, manage, and share your laboratory research activities, fostering collaboration, reproducibility, and efficiency in your scientific workflows.
Differences between a Electronic Lab Notebook and other laboratory solutions
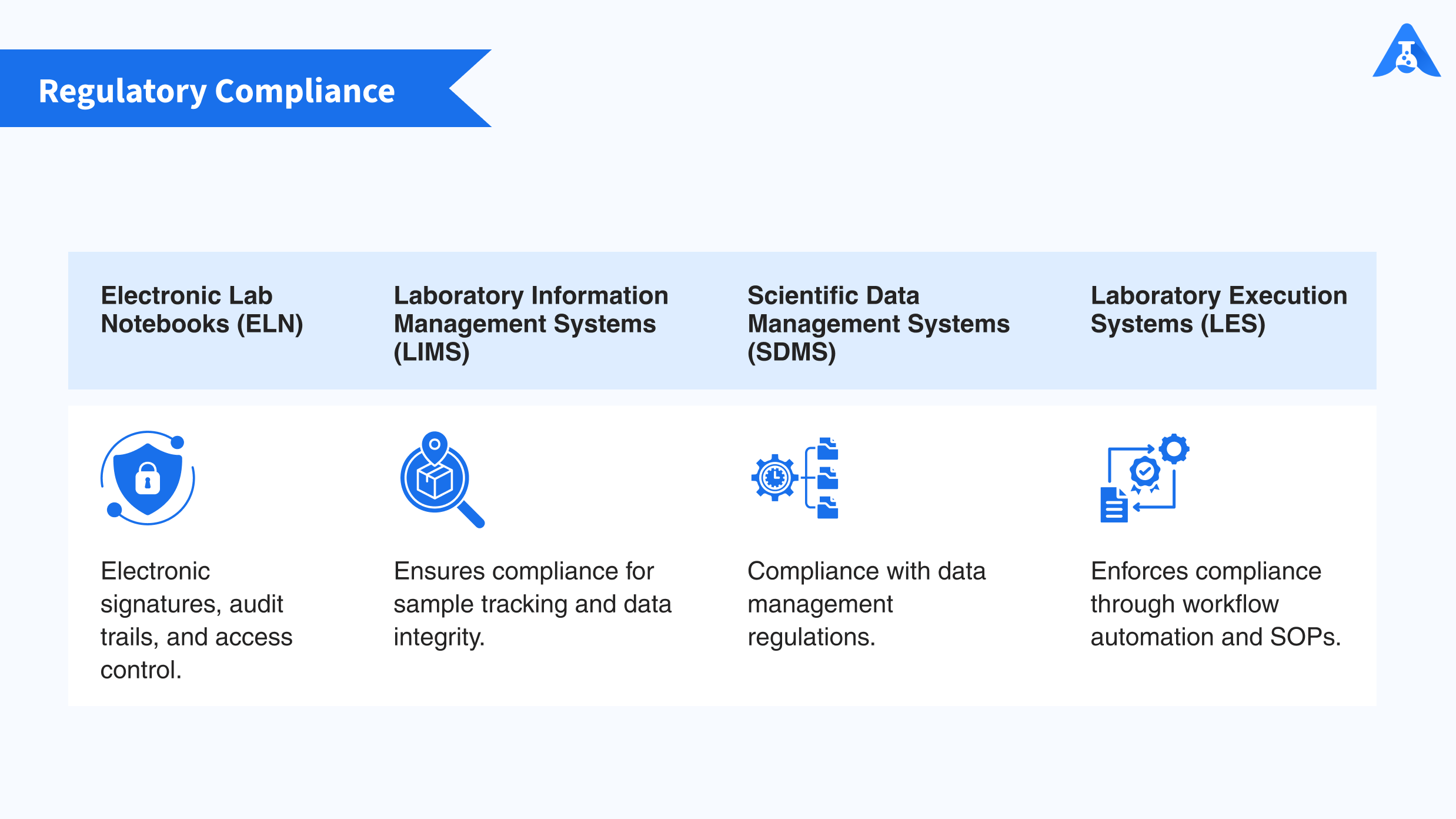
To help you understand the different lab software, here is a comparison of typical software used in a laboratory environment: Electronic Lab Notebooks, Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS), Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS), and Laboratory Execution Systems (LES). This will guide you in choosing the right software for your laboratory needs.
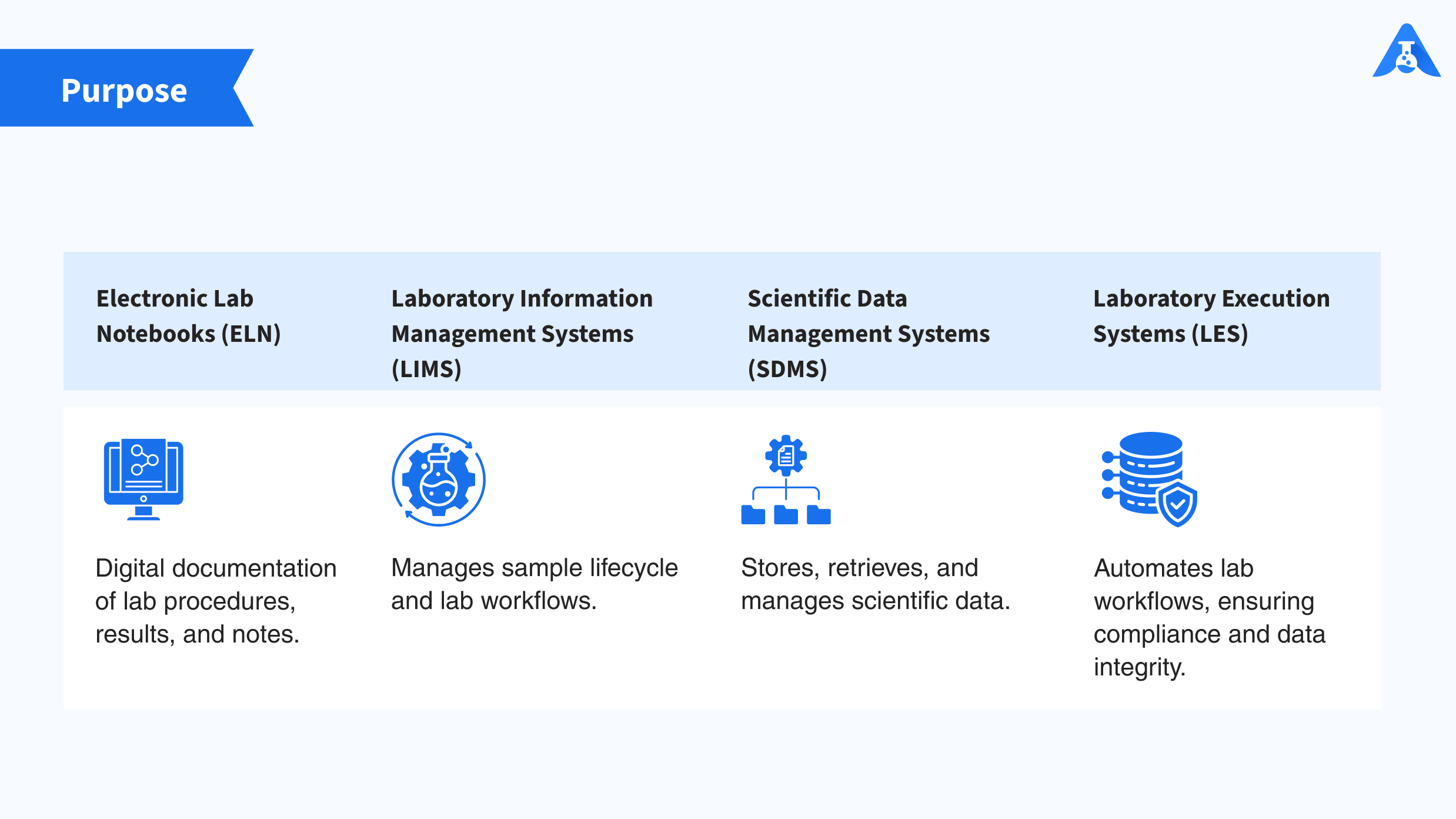
1. Purpose
– Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN): Primarily focused on digital documentation of experimental procedures, observations, and results, aiming to replace traditional paper lab notebooks.
– Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Focuses on sample and data management, tracking sample lifecycle, and managing laboratory workflows.
– Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS): Emphasizes on storing, retrieving, and managing scientific data generated from various instruments and experiments.
– Laboratory Execution Systems (LES): Concentrates on automating and enforcing laboratory procedures and workflows, ensuring compliance and data integrity.
2. Data Management
– Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN): Offers structured data entry, templates, and forms for consistent data recording. Provides version control and search functionalities for efficient data management.
– Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Manages sample and experiment metadata, tracks sample locations, and facilitates sample tracking throughout the laboratory processes.
– Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS): Stores and manages large volumes of scientific data, provides data versioning, indexing, and retrieval capabilities.
– Laboratory Execution Systems (LES): Ensures data integrity by enforcing standard operating procedures (SOPs) and automating laboratory workflows, capturing data in real-time.\
3. Workflow Automation
– Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN): May offer basic workflow templates and automation features for experiment execution and data capture.
– Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Automates laboratory processes such as sample registration, inventory management, and result reporting, enforcing workflow rules and standards.
– Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS): Focuses on data capture and management rather than workflow automation.
– Laboratory Execution Systems (LES): Offers advanced workflow automation capabilities, enforcing SOPs, instrument integration, and real-time data capture.
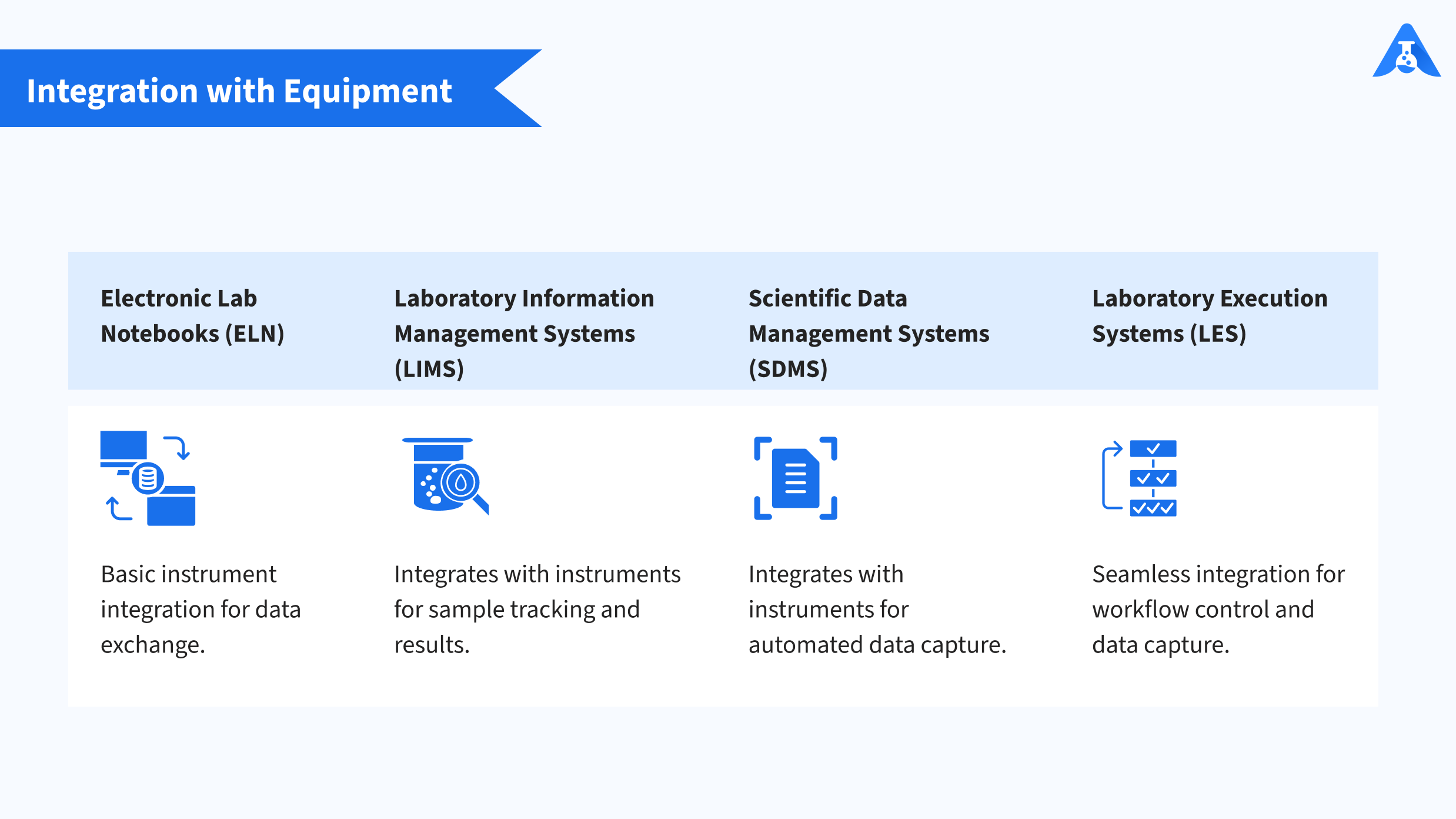
4. Integration with Other Equipment
– Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN): Can integrate with laboratory instruments for data import/export, but may have limited capabilities compared to dedicated integration platforms.
– Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Integrates with laboratory instruments for sample tracking, result capture, and data exchange.
– Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS): Integrates with analytical instruments and software tools for automated data capture and storage.
– Laboratory Execution Systems (LES): Offers seamless integration with laboratory instruments, controlling instrument parameters, capturing data, and enforcing workflows.
5. Regulatory Compliance
– Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN): Provides features such as electronic signatures, audit trails, and access controls to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
– Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Focuses on compliance with regulations related to sample tracking, quality control, and data integrity.
– Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS): Ensures compliance with data management regulations, providing secure storage and access controls.
– Laboratory Execution Systems (LES): Enforces compliance with SOPs, regulatory requirements, and data integrity standards through workflow automation and audit trails.
6. Collaboration
– Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN): Facilitates real-time collaboration among researchers, allowing shared access to experiments and data.
– Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Supports collaboration by providing centralized sample and experiment information accessible to authorized users.
– Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS): Enables collaboration by storing and sharing scientific data among team members.
– Laboratory Execution Systems (LES): Enhances collaboration through shared workflows, real-time data capture, and collaboration tools.
7. Research Data Analysis
– Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN): Provides basic data analysis tools within the notebook, focusing on visualization and basic statistical analysis.
– Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Integrates with data analysis tools for analyzing sample and experiment data stored in the system.
– Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS): Offers tools for managing and analyzing scientific data, including data visualization, mining, and reporting.
– Laboratory Execution Systems (LES): May include built-in data analysis capabilities for real-time analysis of experimental results and process optimization.
8. Documentation
– Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELN): Primarily focuses on documenting experimental procedures, observations, and results within a digital notebook format.
– Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS): Documents sample and experiment metadata, tracking sample lineage and laboratory processes.
– Scientific Data Management Systems (SDMS): Documents scientific data generated from experiments, providing metadata and context for data interpretation.
– Laboratory Execution Systems (LES): Documents laboratory workflows, instrument parameters, and experimental data in real-time, ensuring complete traceability.
In summary, while Electronic Lab Notebooks focus on your digital documentation of laboratory experiments, other laboratory software solutions such as LIMS, SDMS, and LES serve specific purposes related to your sample management, data storage, workflow automation, and regulatory compliance. The choice of software depends on your specific needs and priorities in the laboratory, such as your data management, compliance requirements, collaboration, and workflow automation.
Stakeholders Who Reap the Benefits of an Electronic Lab Notebook
The implementation and use of Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELNs) provide numerous benefits to various key individuals, organisations, and industries involved in laboratory research and development.
Research Organisations
Scientists: When researchers had to rely on paper notebooks, it was cumbersome, prone to loss, and difficult to share with colleagues. Electronic Lab Notebooks revolutionise this process for researchers, which offers a centralised platform for recording, organising, and sharing experimental data, protocols and observations. It’s a streamlined and collaborative way to document your scientific journey, ensuring data integrity and reproducibility.
Laboratory Technicians: The days of technicians juggling stacks of paper forms, painstakingly documenting procedures and tracking samples are far gone with Electronic Lab Notebooks. They can efficiently document experimental procedures, track sample information, and manage laboratory workflows using Electronic Lab Notebooks. Automated data capture and integration with laboratory instruments save time and reduce manual errors, allowing you to focus on the science, not the paperwork.
Academic Institutions
Research Laboratories: As a researcher, Electronic Lab Notebooks can benefit your research laboratories processes by modernising their data management practices, facilitating collaboration among researchers and enhancing the reproducibility of scientific experiments. ELNs also provide a platform for teaching and training students in good laboratory practices.
Universities and Colleges: Electronic Lab Notebooks modernize and support educational activities by providing students with hands-on experience in digital data recording, analysis, and collaboration. This equips academicians with the skills to work on their research projects, thesis work, and scientific publications using the valuable tools offered by ELNs.
Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Companies
Drug Discovery and Development: These companies use Electronic Lab Notebooks to streamline drug discovery workflows, manage vast amounts of experimental data, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. ELNs improve research productivity, accelerate decision-making, and support intellectual property management.
Quality Control and Assurance: Electronic Lab Notebooks help companies maintain quality standards by documenting laboratory procedures, tracking sample information, and ensuring data integrity and traceability. They facilitate audits, inspections, and compliance with Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP).
Chemical and Materials Science Industries
Chemical Research and Development: These industries leverage Electronic Lab Notebooks to record synthesis protocols, characterise materials, and analyse experimental results. ELNs enhance collaboration among chemists, improve data management practices, and accelerate innovation in product development.
Material Testing and Analysis: Electronic Lab Notebooks support material testing and analysis by documenting testing procedures, capturing analytical data, and generating reports. They improve data traceability, facilitate data sharing with clients and regulatory authorities, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Government and Regulatory Agencies
Regulatory Compliance: Government agencies responsible for regulating scientific research and product development benefit from Electronic Lab Notebooks by ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, such as data integrity, traceability, and confidentiality. Electronic Lab Notebooks provide audit trails, electronic signatures, and access controls to support regulatory inspections and audits.
Research Funding Organisations: Funding agencies use Electronic Lab Notebooks to monitor research progress, evaluate project outcomes, and assess the reproducibility and reliability of scientific findings. ELNs enhance transparency, accountability, and data sharing among research grantees.
Overall, the implementation and use of Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELNs) offer you significant benefits if you are a researcher, an academician, academic institutions, industry sectors, and regulatory agencies. They achieve this by improving data management, collaboration, compliance, and innovation in laboratory research and development.
Importance of Electronic Lab Notebooks for Laboratory processes
Electronic Lab Notebooks address various issues that can be faced while using traditional paper notebooks in the lab. The importance of ELN in lab management cannot be overstated. Below, you can find several key reasons why ELN is crucial for effective lab management:
1. Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Electronic Lab Notebooks support compliance with regulatory standards and industry guidelines by providing features such as electronic signatures, access controls, and data encryption. This can ensure data traceability, confidentiality and compliance with Good Laboratory Practices (GLP), Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and other regulatory frameworks in your lab.
2. Facilitated Intellectual Property Management: Electronic Lab Notebooks assist you with securely recording and protecting intellectual property (IP) assets, such as experimental protocols, research findings, and inventions. By documenting laboratory activities in a secure digital environment, your laboratories can safeguard their IP rights and support patent applications and technology transfer initiatives.
3. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication: Electronic Lab Notebooks facilitate collaboration, which enables you to share experimental data, protocols, and results in real-time, fostering teamwork, knowledge sharing, and interdisciplinary collaboration. Collaborators can access and contribute to experiments remotely, regardless of location.
4. Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Electronic Lab Notebooks streamline laboratory workflows by reducing manual data entry and automating repetitive tasks, saving you valuable time and increasing productivity. Features such as templates, forms, and search functionalities can help you to quickly document experiments, analyse data, and make informed decisions.
5. Standardizing Templates and Formats: Electronic Lab Notebooks provide standardized templates and formats for experiment documentation, ensuring consistency and compliance with laboratory protocols and industry standards. This promotes uniformity in data recording practices and facilitates data analysis and interpretation.
6. Automated Workflows: Electronic Lab Notebooks automate laboratory workflows by defining and executing predefined procedures and tasks. This streamlines experiment setup, data capture, result analysis, and reporting, reducing manual errors and enhancing efficiency.
7. Support for Data Analysis and Decision-Making: Electronic Lab Notebooks integrate with data analysis tools and software platforms, which will enable you to analyse experimental data, visualise trends, and make data-driven decisions. By providing a seamless workflow from data capture to analysis, ELNs empower researchers to extract meaningful insights from the research data efficiently.
In summary, Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELNs) are crucial for effective laboratory management due to their ability to improve data organisation, integrity, collaboration, efficiency, compliance, IP management, experiment documentation, and data analysis. They serve as indispensable tools for modern laboratories seeking to enhance research productivity, innovation, and reproducibility while meeting regulatory and industry requirements.
Enabling Paperless Laboratories with Electronic Lab Notebooks
The transition from a paper-based laboratory environment to a paperless one through the adoption of Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELNs) is facilitated by various digital automation features that enhance electronic data capture and management, automate workflows, ensure compliance, and promote environmental sustainability. This means that you no longer must scramble for notebooks or worry about using ink for your lab processes. Here’s how ELNs contribute to this transition of leaving behind the use of paper in your lab:
1. Centralised Data Repository
Electronic Lab Notebooks serve as centralised repositories in your laboratory for storing experimental data, protocols and observations in digital format. This allows you to easily retrieve, share, and analyse data across the laboratory or organisation despite the extensive database.
2. Integration with Laboratory Instruments
Electronic Lab Notebooks integrate with laboratory instruments, enabling you to directly capture experimental data into digital format. This eliminates the necessity of manual data collection from multiple instruments, ensuring accurate data values and reduced work.
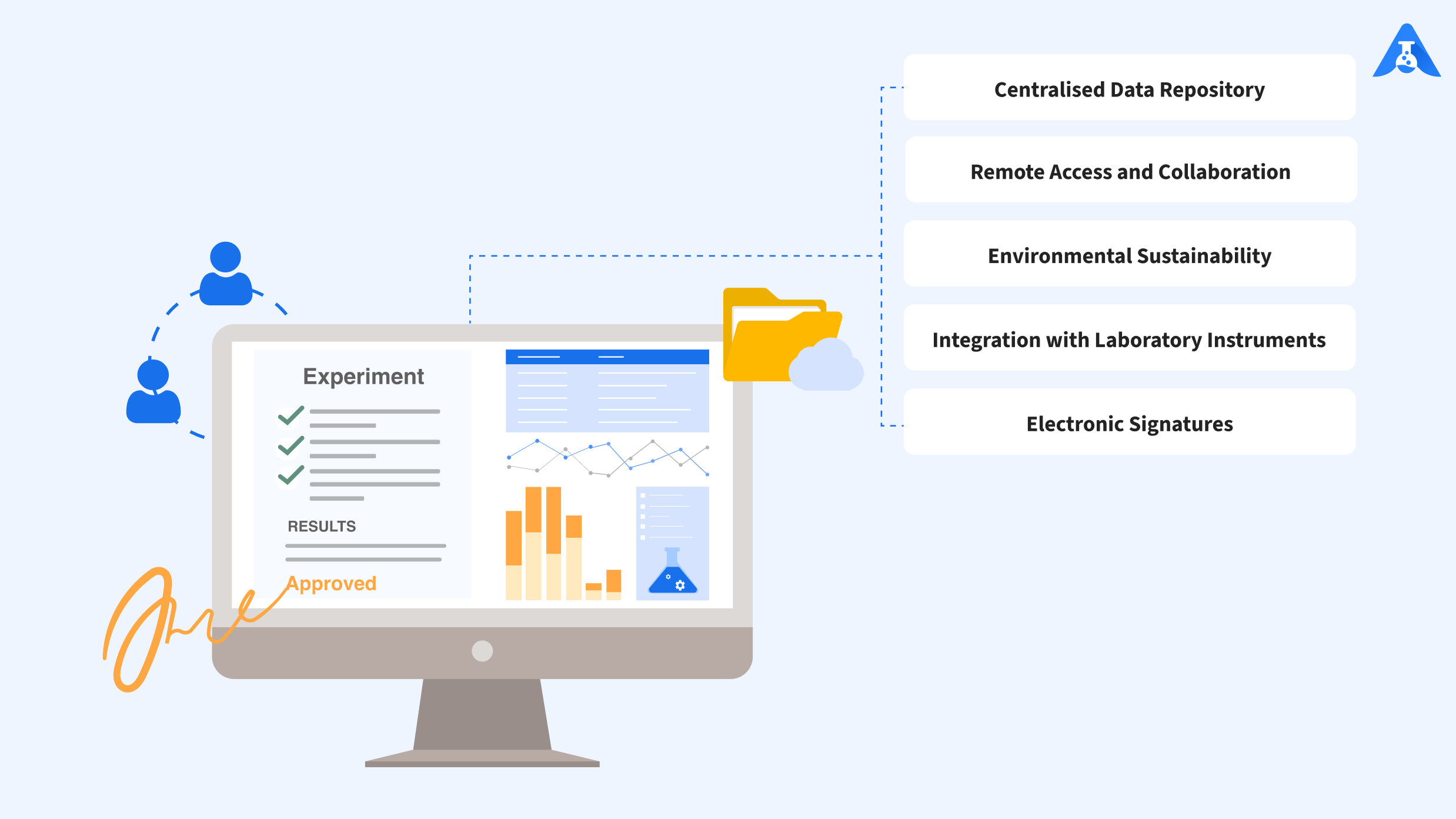
3. Electronic Signatures
Electronic Lab Notebooks let you sign off on experiments electronically to validate and approve records, ensuring data integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements.
4. Remote Access and Collaboration
Electronic Lab Notebooks enable remote access to experiment records and data, which allows you to collaborate with colleagues in real-time, from any location. This promotes collaboration, knowledge sharing, and teamwork among researchers, regardless of geographical barriers.
5. Environmental Sustainability
Electronic Lab Notebooks eliminate the need for paper-based notebooks and documentation, reducing paper consumption and waste generation in your laboratories. This contributes to environmental sustainability by conserving natural resources and reducing carbon footprint.
To summaries, Electronic Lab Notebooks facilitate the transition to a paperless and eco-friendly laboratory environment by leveraging digital automation to enhance data capture and management, automate workflows and ensure compliance. It can streamline your laboratory operations by improving efficiency and enhancing collaboration & data integrity. Thus, it ultimately drives innovation and scientific advancement in your lab operations.
How to adopt Electronic Lab Notebooks and replace legacy applications in a lab
Transitioning from a legacy system to a modern digitised Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) in your laboratory might seem like moving a mountain. However, with these key steps, you will be able to ensure a smooth and successful implementation of the same. Here are detailed steps involved in this transition:
1. Assessment and Planning
Evaluate Current System: First, you will have to assess the strengths and limitations of the existing legacy system in your lab. This includes workflows, data management practices and user requirements.
Define Goals and Objectives: What are you hoping to achieve with an Electronic Lab Notebook? Identify the key objectives and desired outcomes of transitioning to modern software. You may consider factors such as improving data accessibility, enhancing collaboration, ensuring compliance, and increasing efficiency.
Stakeholder Engagement: Getting all the stakeholders from different departments and roles in the laboratory is vital. You will need the input and support of all your key lab players, including researchers, IT staff, administrators and management for the transition.
2. Requirements Gathering
Identify User Needs: Think of this like creating a wishlist from end-users like researchers, technicians and administrators. Collect information on requirements such as functionality, usability and integration that are needed for the new Electronic Lab Notebooks system.
Define Technical Requirements: You will need to determine the technical requirements for the ELN system. This includes compatibility with your existing IT infrastructure, integration with lab instruments, data security, scalability, and support for regulatory compliance.
3. Selecting Your Vendor
Market Research: Make sure to explore the Electronic Lab Notebooks market and identify potential vendors who offer solutions that align with your lab’s needs and budget.
Request for Proposals (RFPs): Develop a Request for Proposals (RFP) or Request for Information (RFI) document that outlines your lab needs and solicit proposals from ELN vendors.
Vendor Evaluation: Carefully evaluate the vendor proposals that you receive based on functionality, cost, support services, reputation, and track record. Consider conducting demos and obtaining references from other customers, before proceeding forward.
4. System Configuration and Customization
Installation and Setup: You will have to work with the chosen ELN vendor to install and configure the new system according to your laboratory’s requirements and specifications.
Customization: It is important to tailor and customise the ELN system to align with your specific laboratory workflows, data structures, and user preferences. This may involve configuring templates, forms, workflows, and user permissions.
5. Data Migration
Data Inventory: Make sure to take stock of all the existing data stored in our legacy system, including experiment records, protocols, sample information, and any metadata.
Data Mapping: Mapping between data fields and structures from your old system to the corresponding fields in the new ELN system must be established. This will ensure that all your scientific information is transferred accurately, retaining data integrity and consistency.
Data Migration: While transferring data from the legacy system to the new Electronic Lab Notebooks platform, you can use automated migration tools or manual processes. The most important thing, however, is to validate the migrated data to ensure its accuracy and completeness.
6. Training and User Adoption
Training Program: Developing a comprehensive training programme to get end-users familiar with the features and functionalities of your new ELN system is crucial. The implementation of this ELN bootcamp will help in familiarising yourself with the features, functionalities, and workflows of the new ELN system. Providing training sessions, user guides, and online resources will support user adoption and make it easier for everyone to navigate this new system.
User Feedback and Support: Opening communication to actively solicit feedback from users during the training and initial rollout phases is key. This way, you can identify any roadblocks or challenges. Providing ongoing support and assistance will help with addressing anything that concerns or confuses users, ultimately optimising the system’s usability.
7. Testing and Validation
System Testing: Conducting rigorous testing of the new ELN system will help to identify and resolve any bugs, errors, or compatibility issues. Functionality, performance, security and integration with other systems – make sure everything runs smoothly in the new environment.
Validation: This is essential, for it ensures compliance with regulatory requirements, such as GLP, GMP and data integrity standards. You will need to document the validation procedures and results for future regulatory audits, ensuring accuracy.
8. Rollout and Deployment
Pilot Deployment: Before full deployment, you must implement the new ELN system at a small scale, as a pilot project. A select group of users or laboratory departments will get a sneak peek of the new system. Gather feedback and assess the system’s performance & usability.
Full Deployment: Once the pilot phase is a success, roll out the ELN system to the entire lab or organisation. Communicate rollout plans, provide comprehensive training and support, and continuously monitor user adoption & feedback.
9. Continuous Improvement
Monitoring and Evaluation: The journey doesn’t end after launch. You will need to continuously monitor the performance, usage and effectiveness of the ELN system after deployment. Collecting user feedback from researchers and stakeholders is crucial for identifying areas for improvement and optimization.
Iterative Enhancements: Based on user feedback, implement iterative enhancements and updates to the ELN system. Make a note of the changing requirements and technological advancements. Work closely with the ELN vendor to implement new features, address any lingering issues and stay up to date with industry best practices.
10. Documentation and Knowledge Transfer
Make sure you document the transition process, including requirements, implementation steps, configurations, and lessons learned. This documentation of the journey, along with training materials, will serve as a valuable resource for future reference.
Transfer knowledge and expertise gained during the transition to internal staff or designated administrators. These individuals will be responsible for managing and maintaining the ELN system going forward. This ensures that the lab functions proceed to thrive and allow the next ‘generation’ of users to become experts too.
To make sure you make the right choice with an Electronic Lab Notebook, you may consider Agaram’s Logilab ELN. This Lab Notebook ticks important points that have been mentioned so far and offers reliable and integral functions in your lab. With its user-friendly design, Logilab ELN fosters collaboration and ensures that all your research data is captured flawlessly. Focusing on the scientific journey of discovery using Logilab ELN will help you with not getting swamped with tedious paperwork. Logilab ELN prioritizes both regulatory compliance and data security, empowering you to record, analyse, and collaborate with ease, ultimately propelling your lab to the forefront of scientific progress.
By following these steps systematically, your lab can thus successfully transition from a legacy system to a modern digitised Electronic Lab Notebook (ELN) system. This will efficiently improve data management, collaboration, efficiency, and compliance in laboratory research and development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Electronic Lab Notebooks (ELNs) usher in a new era of scientific exploration. They have revolutionised laboratory operations by transforming traditional paper-based processes into efficient, digitized workflows. It offers features like structured data entry, version control, and electronic signatures, making data management a breeze. Collaboration flourishes as researchers can co-author experiments and access information seamlessly, just like working on a shared online document. This is possible all the while ensuring regulatory compliance.
The benefits of Electronic Lab Notebooks extend beyond improved efficiency to include enhanced data integrity and accessibility, fostering a foundation of trust and transparency in research. Sustainability too gets a boost, for paper lab notebooks become relics of the past. By providing a centralised platform for experiment documentation and data analysis, the software empowers you to focus on the real goal, which is scientific discovery and innovation. As laboratories continue to embrace digital transformation, Electronic Laboratory Notebooks are a testament to progress and a catalyst for facilitating collaboration in research endeavors.